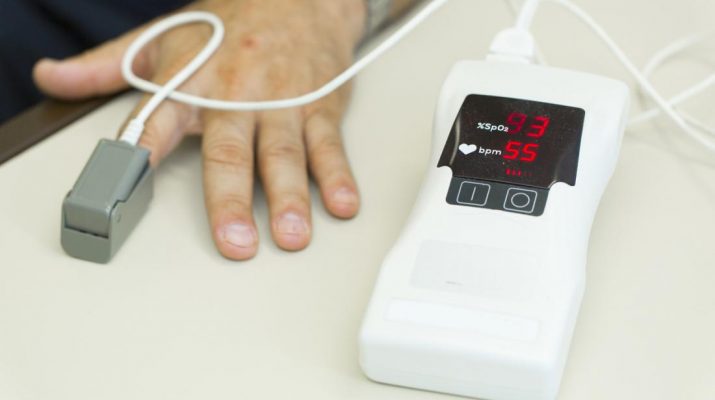
Introduction:
Pulse oximeters are medical instruments that measure oxygen saturation i-e how much hemoglobin present in the blood is bound to oxygen. It is an instrument that is used very commonly in hospital settings and is available in the operation theatre, ambulance, ICY, and critical care wards.

What is Oxygen saturation?
Before understanding how does a pulse oximeter sensor work, it is important to understand the concept of oxygen saturation.
Oxygen is required by the cells of the body for their normal functioning. Blood carries oxygen from the lungs to body cells. Hemoglobin is a component of red blood cells that has the ability to bind oxygen and carry it. Oxygen saturation is the measure of the hemoglobins that are currently carrying oxygen molecules. The normal oxygen saturation is 33 percent.
Working of Pulse Oximeter:
Hemoglobin is made up of four subunits i-e 2 alpha chains and 2 beta chains. Hemoglobin exists in two forms:
- Relaxed (R) form: It represents the oxygenated form where hemoglobin has a high affinity for oxygen
- Taut (T) form: It represents the deoxygenated form where hemoglobin has a low affinity for oxygen.
The significance of the T and R forms lies in the fact that they lead to different electromagnetic absorptions and hence, different emissions of light.
Principle Pulse Oximeter:
The working of a pulse oximeter is based on the different absorptions and emissions of light by T and R forms of hemoglobin.
Instrument Parts:
A pulse oximeter consists of
- An electronic processor
- Two LED lights facing a photodiode.
The LED lights face the photodiode through a translucent part of the patient’s body like an ear lobe or a fingertip.
One LED light is red and has a wavelength of 660nm and the other is infrared with a 940 nm wavelength.
The absorption of light by oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobins is different at different wavelengths of light. Oxygenated hemoglobin absorbs more than 940 nm of light and allows 660 nm of light to pass through it. Whereas, deoxygenated hemoglobin absorbs the red light and lets the infrared light pass through it.
Working of Pulse Oximeter:
A pulse oximeter measures the light that is transmitted. The measurement fluctuates because the arterial blood is moving with each heartbeat. Subtraction of peak transmitted light from minimum transmitted light allows the correction of other tissues since only arterial blood is measured.
The electronic processor calculates the ratio of red light measurement to infrared light measurement which is a direct measure of the ratio of oxygenated blood to deoxygenated blood in the patient’s arteries.
The processor then uses the Beer-Lambert law to calculate the SpO2 reading.
Interpretation of Results:
The oxygen saturation in the form of the ratio of oxygenated hemoglobin to deoxygenated hemoglobin is an important measure of whether a patient’s body is able to transfer oxygen from the lungs into the bloodstream. The saturation measured by oximeter does not tell anything about the tissue saturation i-e even 100 percent oxygen saturation in the blood does not guarantee the oxygenation of tissues. An oximeter only measures the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.