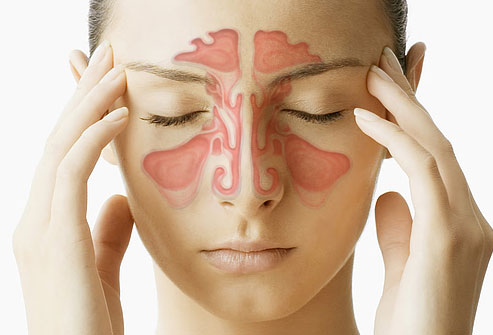
You have a runny nose, a headache, discomfort under your eyes and around your nose, and possibly a cough when you wake up. It’s obvious to worry whether you have a cold or a sinus infection. Colds can develop into sinus infections since they are both caused by viruses. However, germs can induce a sinus infection in some cases.
Sinuses are the hollow chambers located within the cheekbones, forehead, and between the eyes. These passageways’ linings can enlarge, causing mucus to build up. After acquiring a cold, many people acquire a sinus infection caused by the rhinovirus. Cold symptoms such as a runny nose and congestion can promote inflammation and avoid the sinuses from emptying normally. When you have a viral sinus infection, you cannot spread the infection to others, but you can transmit the virus to others. Someone who contracts the virus from you is more likely to acquire a sinus infection as well. You may be contagious for two weeks.
Cause of Sinus Infections
Sinus infections are also medically known as rhinosinusitis and sinusitis. Since most of the infections are contagious, practitioners do not agree with the contagiousness of sinus infections.
Because bacteria and viruses (and, on rare occasions, fungi) are the most common causes of sinus infections, some specialists believe that the bacteria, viruses, or fungi can be passed from person to person and cause sinus infections. According to other specialists, sinus infections arise because the conditions in the individual’s sinuses are ideal for infection, even though they are caused by bacteria and viruses.
Furthermore, the infection can be induced by bacteria, viruses, or fungi that are already present in a person and do not require transmission from one person to another. However, the majority of doctors believe that, except in exceptional cases, most people do not spread sinus infections, and hence conclude that sinus infections are not contagious.
Even if the disease, sinusitis, is not, there is universal agreement that bacteria, fungus, and/or viruses are passed from person to person. Individuals with sinus infections should avoid direct contact, such as kissing, with those who are more susceptible to infection, such as infants, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems, to reduce the risk of spreading bacteria, fungi, and viruses to others, which can cause problems besides sinus infections. Sinusitis is caused by viral or bacterial germs that live inside a person’s body.
How to know if a person is infected with a sinus infection? What are the symptoms?
Sinus infections typically begin with cold-like symptoms such as a runny nose, cough, and/or slight fever, and progress to discomfort and pressure in the sinus cavities. Other symptoms that signal you may have a sinus infection appear 7 to 10 days after you first experience cold-like symptoms.
Sinus infection symptoms include:
- A yellowish-greenish nasal discharge that could have an odor
- Puffiness around the eyes
- Bad breath
- Coughing
- Pressure in the sinuses
- Sinus headaches
These symptoms are not the same for all. Most individuals with sinusitis or sinus infection may also develop symptoms and signs like:
- Sore throat
- Fatigue
- Earaches
The patient’s history, medical examination, and signs of sinus inflammation, which can be seen on X-rays or a CT scan of the sinuses, are used to make a definitive diagnosis of a sinus infection.
How long do the sinus infections symptoms last?
- If the signs and symptoms of acute sinusitis or sinus infections go away, they endure about three weeks.
- Recurrent sinusitis is acute sinusitis that happens more than once a year and can progress to chronic sinusitis.
- Chronic sinusitis, often known as sinus infections, can linger for up to eight weeks.
How long do sinus infections stay in the body? Are they curable?
When the symptoms of a sinus infection stop, usually after 3 weeks, the person is said to have been cured. However, in some patients who have chronic or repeated sinus infections, a cure is just temporary. Antibiotics may help with bacterial sinus infections often long-term antibiotic treatment is needed before a patient is considered cured of bacterial sinusitis, but there is no such treatment for viral sinusitis.
What is the treatment for sinus infections and how are they?
Many virus-caused sinus infections will clear up on their own without the need for medications. This is significant because using antibiotics when you don’t need them might result in negative effects and long-term resistance. Antibiotics will almost certainly be required if the infection is caused by bacteria.
Your doctor may ask you to use over-the-counter drugs to aid with your symptoms and to keep an eye on your condition.
The examples of over-the-counter medication include:
- Decongestant
- Saline nasal spray
- A warm compress on the forehead and nose to relieve sinus pressure
- Acetaminophen or ibuprofen to soothe the pain.
What medications lessen the pain, help relieve other symptoms?
Pain relievers for pain and other sinus infections symptoms are:
- acetaminophen (Tylenol and others) and
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), for example, ibuprofen [Advil and Motrin] and naproxen [Aleve]).
Most people get sinus infections as a result of other illnesses. Asthmatics, for example, have narrowed airways and are more likely to develop sinusitis. Prescription asthma treatments may lessen the likelihood of developing sinusitis.
When is surgery the best option for sinus infections and sinusitis?
Some patients with the following conditions may require surgery or other procedures to open up restricted or clogged nasal or sinus passages:
- Chronic sinus infections or sinusitis
- A deviated septum
- Nasal polyps
- A deviated septum in the nose to relieve sinusitis
When should one seek medical care?
If your symptoms are severe, such as a severe headache or facial discomfort, if your symptoms worsen after initially improving, if your symptoms persist more than 10 days with no improvement, or if you have a fever for more than three to four days, you should get medical help.
When to visit the doctor for sinus infections or sinusitis?
If you acquire a persistent fever, have a history of recurrent or chronic sinusitis, or if your sinus symptoms do not improve or worsen, see your doctor. However, if you have any of the following symptoms, get medical attention right away.
- Confusion
- Severe headaches
- Stiff neck
- Swellings in the forehead and/or eyes
- Shortness of breath.
How a Sinus Infection can be prevented?
Use disinfecting wipes to clean daily touched items like light switches and doorknobs after washing your hands and sneezing &coughing into the nook of your elbow. Also, during the brief period when you may be contagious, keep a safe distance from your healthy family members.
To conclude with…
Drinking enough water, getting enough rest, reducing stress, and cleaning your hands are all important ways to stay healthy. Vaccines, such as the flu vaccine, are highly recommended. Also, refrain from smoking and prevent inhaling second-hand smoke. Doctors advise, stay away from those who have colds or the respiratory illnesses mentioned above.